In this topic, you will learn about Light, Reflection & Refraction, Human Eye & Defects of Vision, MCQs. This topic is very important from the examination point of view.
Also Check: Waves and their types
What is light?
Light is a form of energy, which is propagated as electromagnetic wave. It is the radiation which enables us to see the object around us. Its speed is 3×108 m/s.
Light is a transverse wave. It means it travels in the form of crests and troughs. Light comprises of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, which are perpendicular to each other and also perpendicular to the direction of propagation of light.
Light takes 8 min 19s to reach on the earth from the sun and the light reflected from moon takes 1.28s to reach earth.
Light consists of seven lights, which are Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red (remembered as VIBGYOR). The Red light has the maximum wavelength and the Violet light has the least wavelength.
Primary Colors
There are three Primary Colors. They are Blue, Red, Green.
Secondary Colors
Secondary Colors- The coloured produced by mixing any two primary colors.
Complementary Colors
Any two colours when added produce white light. Example; Red and Green, Yellow and Purple.
Reflection of light
When light bounces back after striking a surface, it is called reflection of light. In reflection, the light comes back into the medium of incidence.
Laws of reflection
There are two laws, that govern reflection of light. They are:
- Angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
- The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal, all lie in the same plane at the point of incidence.
Reflection of light allows you to see yourself in the mirror.
Remember that velocity, frequency and wavelength remain unchanged during the reflection of light.
Reflection of light from a plane mirror
When light gets reflected from a plane mirror, then;
- The distance of image from mirror is equal to the distance of object from the mirror.
- The image produced is virtual.
- The image has the same size as that of the object.
- Magnification is equal to 1. (Magnification= size of image/size of object)
Refraction of light
When light travels from one medium to another, which are optically different than one another, it deviates from its path. This phenomenon of deviation/bending in the path of light is called refraction of light.
Remember, that speed of light changes on going from one medium to another. Among the two medias, the medium in which speed of light is more is called an optically rarer medium or simply rarer medium, and the medium in which speed of light is less, is called optically denser medium or simple a denser medium.
When light goes from a rarer medium to a denser medium, it bends towards normal, and when it goes from a denser medium to a rarer medium, it bends away from the normal.
Laws of refraction;
Refraction is governed by two laws. They are:
- First law: It is known as Snell’s law. According to it, the ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is always constant. This constant is known as Refractive index. Refractive index is a dimensionless and unit less quantity. It is simply a number.
- 2nd law: The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal, all lie in the same plane at the point of incidence.
Consequences of refraction.
- Bending of a stick when put in a tub filled with water.
- A coin placed at the bottom of a water filled tub seems to be raised.
- A water filled tub seems to be shallower than when it is empty.
- formation of two images.
Remember that during refraction of light, the velocity and wavelength change where as the frequency remains unchanged.
Human Eye
The human eye works on the refraction of light through a natural convex lens. This lens is made of transparent living material and enables us to see things around us. The thickness of this lens varies according to situations in which an eye is placed.
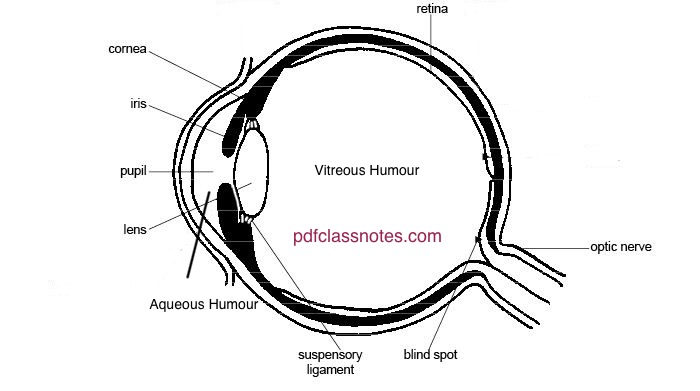
Least distance of distinct vision for human eye is 25 cm.
Defects of vision
1. Myopia
This is also called shortsightedness. In this defect, an eye can see nearby objects clearly but not the far objects.
In myopia, image is formed before retina and It can be corrected by using a concave lens of suitable focal length.
2. Hypermetropia
It is also called hyperopia or longsightedness. In this defect, an eye can see far off objects clearly, but not the nearby objects.
In Hypermetropia, image is formed behind retina and it is corrected by using a convex lens of suitable focal length.
3. Presbyopia
It is also called old age hypermetropia. In this defect, an eye can not see both nearby and far off objects clearly.
MCQs on Light and Optics For competitive Exams
Now is the turn to solve some important MCQs on light, Reflection and Refraction. Lets go.
1. A light ray coming from a denser medium hits the interface at an angle equal to the critical angle. What happens to it?
- it will go back into the denser medium.
- it will go into the rarer medium and bend away from the normal.
- it will go along the interface.
- it will go normally to the interface.
it will go along the interface.
2. Which of the following is true for occurrence of Total Internal Reflection?
- The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle.
- The light should travel from a rarer medium to a denser medium.
- both of them
- none of them
- only 1
- only 2
only 1, For occurence of Total Internal Reflection, light should come from a denser medium and should strike the interface at an angle greater than the critical angle.
3. Sparkling of diamond is because of:
- Refraction
- Reflection
- Scattering
- Total Internal Reflection
Total Internal Reflection
4. Which of the following parameters of light does not change during refraction of light?
- velocity
- wavelength
- frequency
- All
frequency
5. What is the speed of light in vacuum?
- 300000000 m/s
- 350000000 m/s
- 380000000 m/s
- 305000000 m/s
300000000 m/s
6. What are the units of refractive index of a medium?
- m/s
- kg/s
- kg/cm
- no units
no units
7. A coin placed at the bottom of a water filled tub appears to be raised. It is because of:
- Refraction
- Reflection
- Scattering
- Dispersion
Refraction
8. Which among the following is correct about the reflection of light?
- Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- The velocity of the light decreases after reflection
- The frequency of the light remains constant during reflection.
- all of them
- only 1 and 2
- only 1 and 3
- only 2 and 3
only 1 and 3
9. When light goes from a denser medium to a rarer medium obliquely, What happens to it?
- It bends away from the normal.
- it bends towards the normal.
- it goes straight.
- it goes parallel to the normal.
It bends away from the normal.
10. The phenomenon of bending of light upon changing its medium is known as:
- Refraction
- Scattering
- Reflection
- Dispersion
Refraction
So, this was all about Light, Reflection & Refraction, Human Eye & Defects of Vision, MCQs. We are sure that you have loved this article.